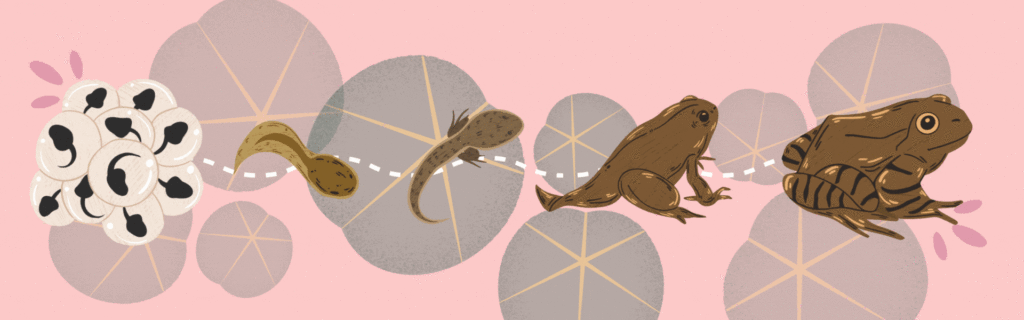
Learn about how small eggs turn into adult frogs!
Life-Cycles of Frogs
Click between the tabs below to learn about the life-cycles of different frogs!
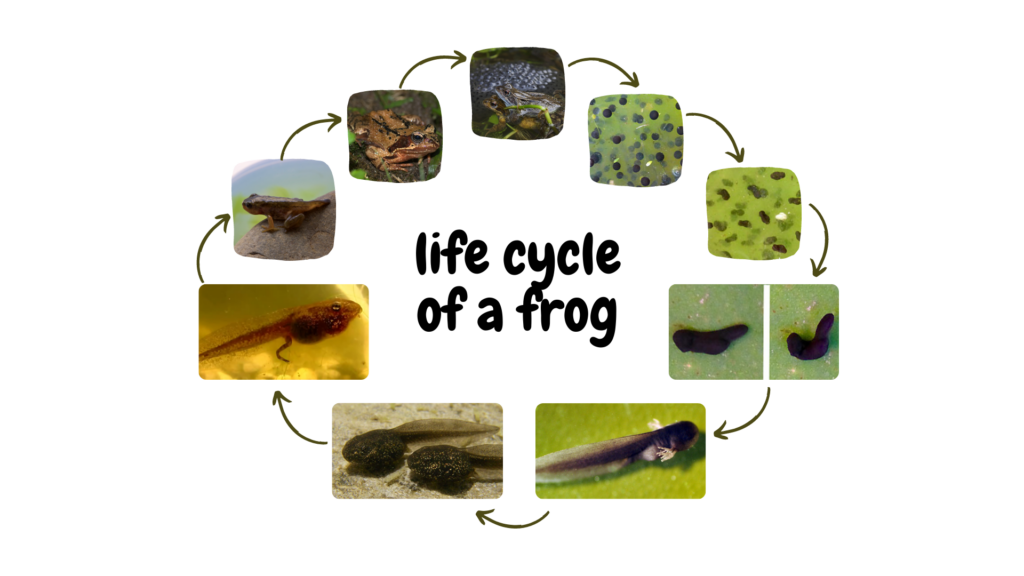
Below is a drawing of the life-cycle of the common frog. The Latin name for this frog is Rana temporaria. During its life cycle, the common frog physically transforms from a hatchling tadpole to a fully grown frog! Another more scientific name for this process is metamorphosis, which translates to “changing shape”.
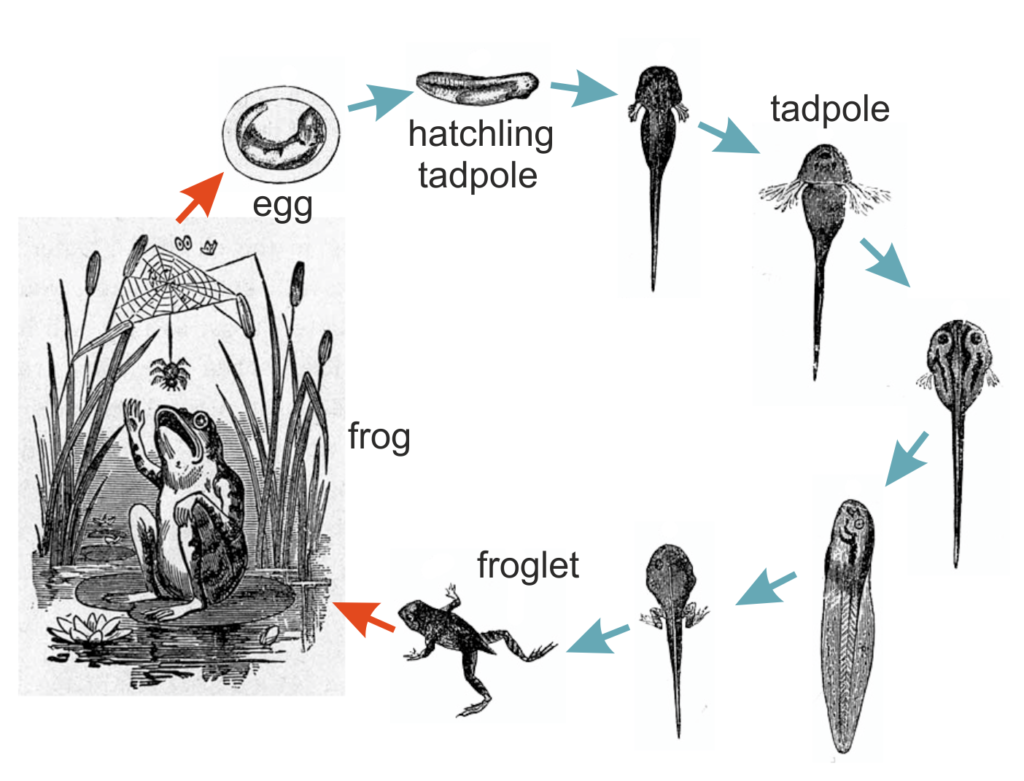
In our lab, we focus our studies on the African clawed frog. The latin name for this frog is Xenopus laevis. Xenopus have very similar life-cycles to the common frog, but there are a few important differences. Xenopus tadpoles eat different food to common tadpoles and adult Xenopus frogs are also fully aquatic!
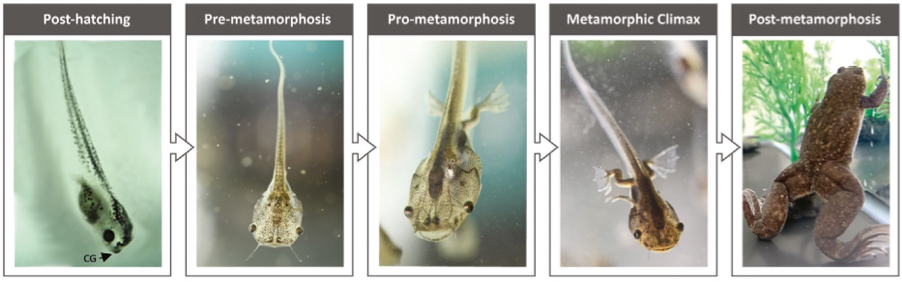
Detailed Life Story of the Common Frog
Click on the images below to follow the life-cycle of the common frog!
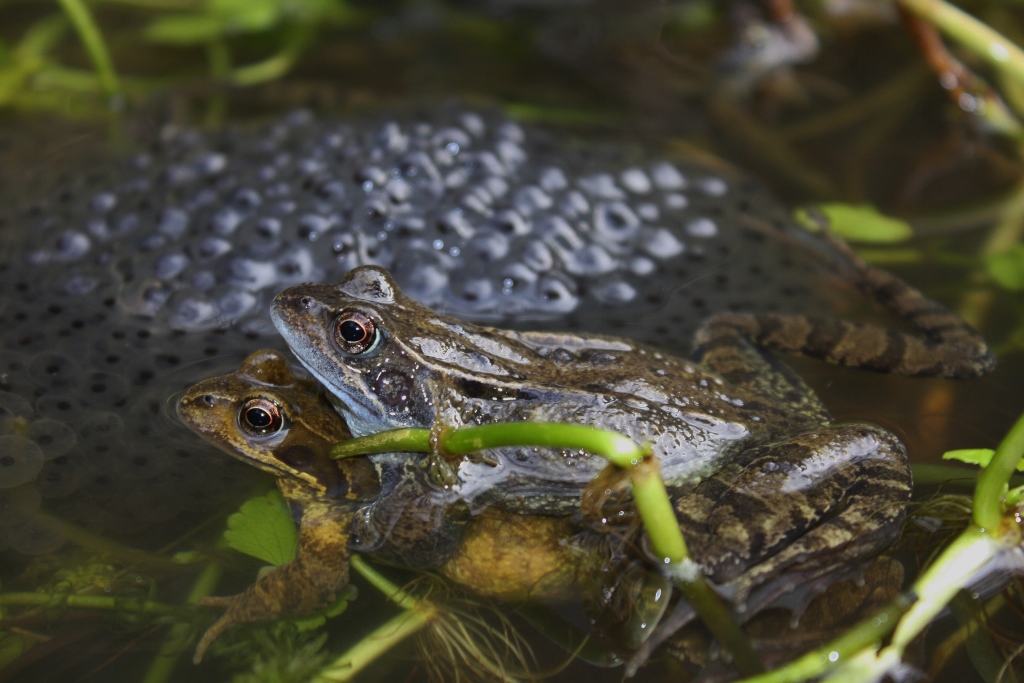
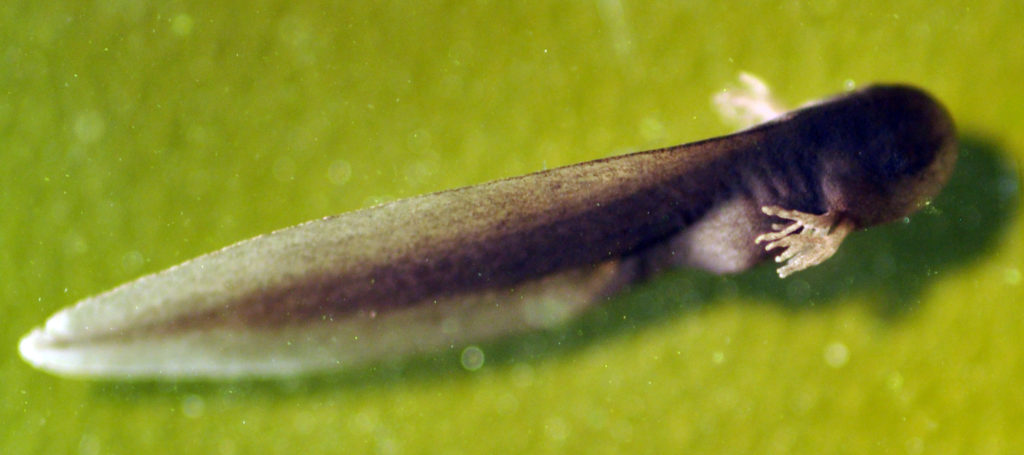
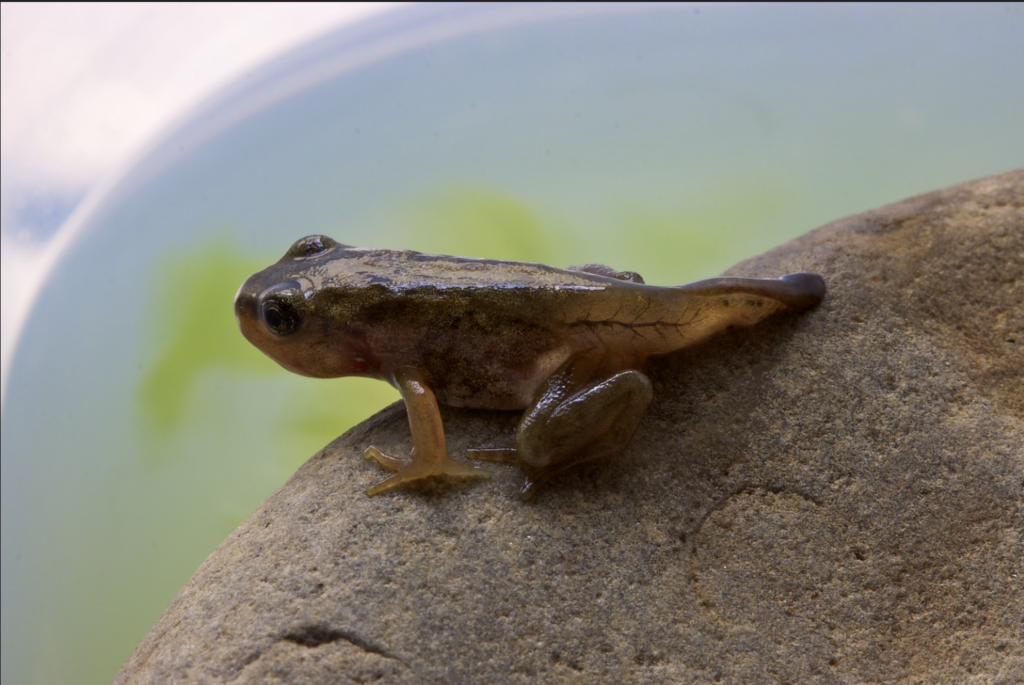
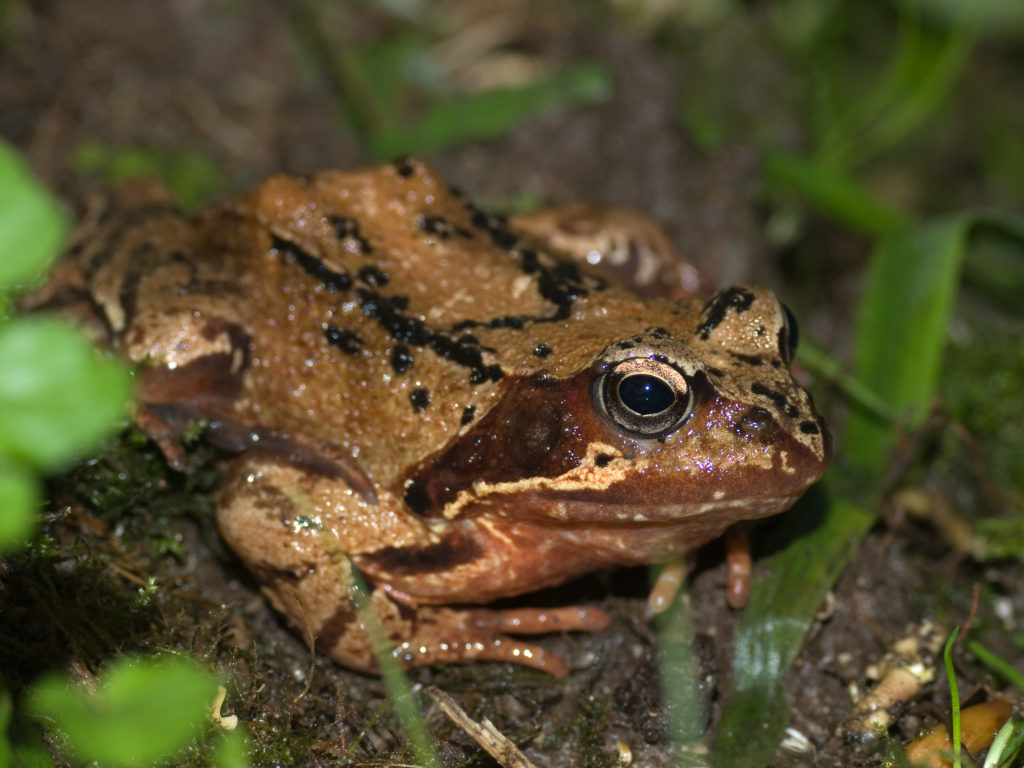
















Now let’s summarise what we’ve just learnt!
You can also watch this video which summarises the metamorphosis of a frog!
What About Other Frogs?
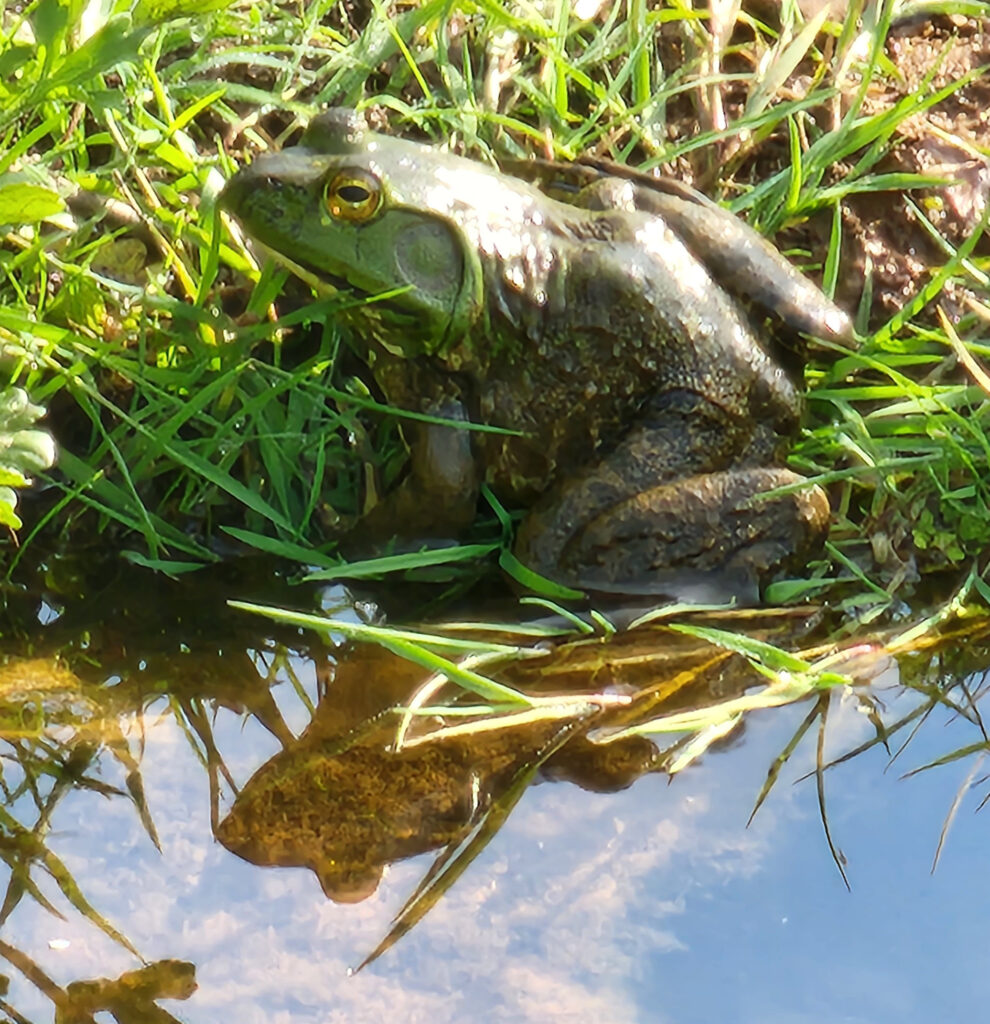
The American bullfrog (Latin name: Lithobates catesbeiana) has a very similar life-cycle and metamorphosis to the common frog, but not all frogs develop this way.

The Puerto Rican coqui tree frog (Latin name: Eleutherodactylus coqui) develops completely in its egg! This is called direct development1. Unlike the common frog, they hatch as fully formed froglets, often with small tails. Watch these two videos below of coqui frogs hatching!
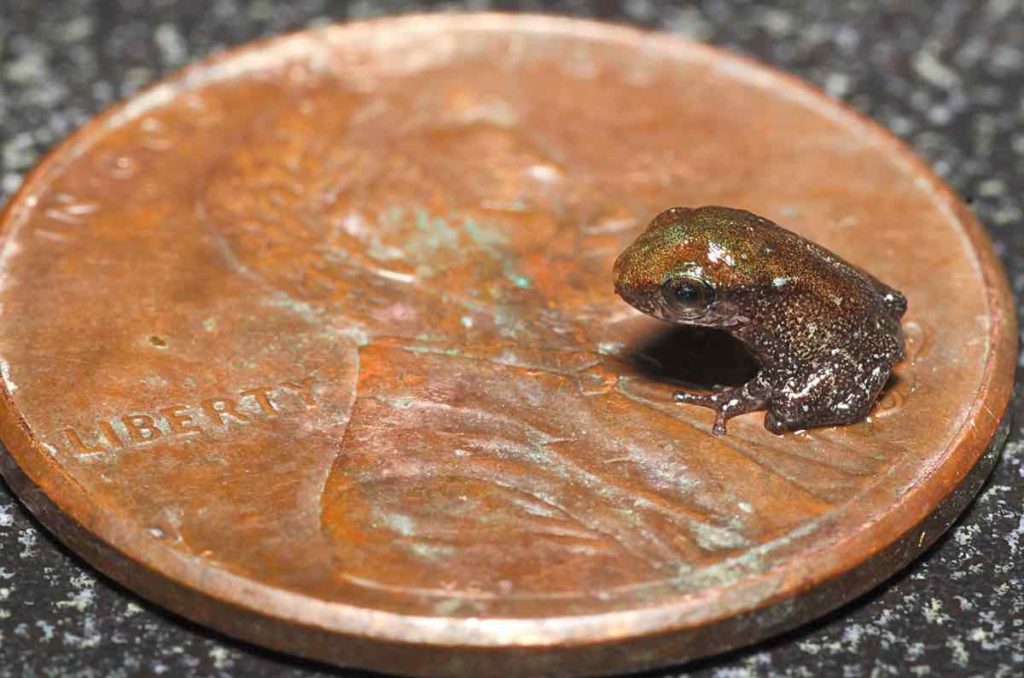
Because of this direct development, their eggs have to be much larger than the eggs of the common frog, so that they have enough nutrients to fully develop before they hatch. It also means they are very small frogs. Look at this adult coqui frog- it fits onto a US penny!

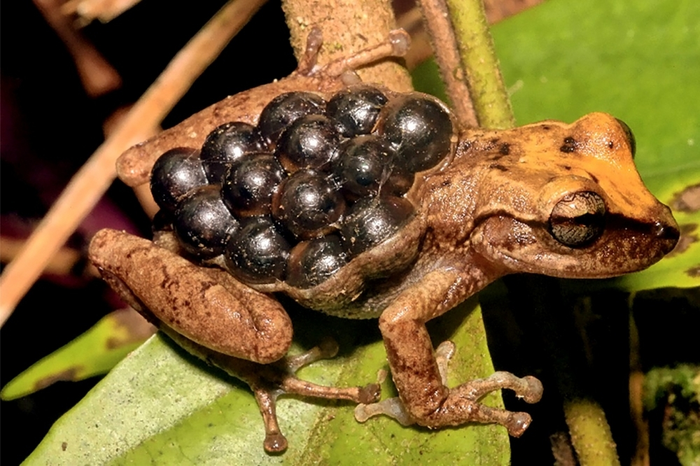
So-called marsupial frogs have the biggest eggs of all the frogs, with eggs measuring up to 10mm in diameter. Unlike other frogs, mother frogs have a pouch on their back where the eggs develop1. You can spot a female marsupial frog if you see little eggs or tadpoles on a frog’s back!

Darwin’s frog (Latin name: Rhinoderma darwinii) is a small frog native to Argentina and Chile with an especially unique life-cycle. After the male and female have mated and ferlitised eggs hatch into tadpoles, the male frog swallows the young tadpoles! He places them in a special pouch in his throat called a vocal sack2. After the tadpoles have fully developed into little froglets, the father has to spit them out! This is where this frog has gotten its nickname as the ‘vomit frog’. Watch the video below to see this unique frog in action!
Quiz Time!
Results
We hope you now know more about the life cycles of tadpoles! Click here to explore more topics.
#1. What is the scientific name of the process of when a tadpole changes into a frog?
#2. What is the first step in the common frog’s life cycle?
#3. When tadpoles first hatch, how do they swim through the water?
#4. Click on the image of a froglet.
#5. What is the name of the frog that can fit onto a penny when it is a fully grown adult?
Fun Activities
Click through the different tabs below to see the different fun frog activities we have for you!
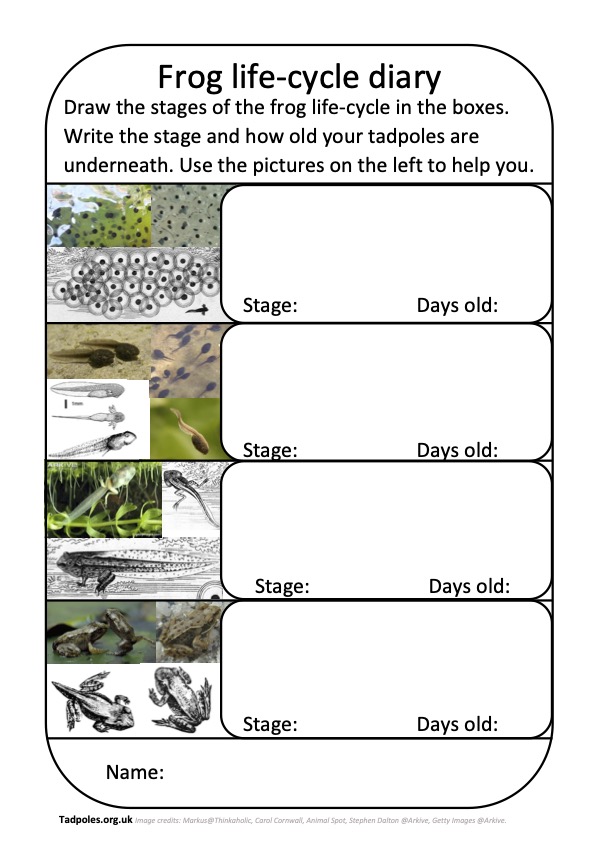
Do you want to see how tadpoles develop in real-life? Click here to download a life-cycle diary that you can fill out as your tadpoles grow!
Listen to a song about metamorphosis by the Singing Zoologist! See if you can match the stages we talked about above to his lyrics.
Click here to download a colour-in activity of a frog.
Watch the video below to see how Samiah Rose tracked her tadpoles’ development into frogs, and maybe you can try making your own video too!
Remember to attribute photographs, videos or work where appropriate! This is not needed unless used online, but if you’re unsure please refer to the creative commons licence rules. For academic references and media credits of the images above, please refer to the next page.





