Find out what tadpoles eat at different stages of their life-cycle.
You Are What You Eat?
Animals can be sorted into groups based on what they eat. They can also eat different things at different stages throughout their lives.
Carnivores
Animals that only eat meat

Omnivores
Animals that eat plants and meat
Herbivores
Animals that only eat plants
Food in a Tadpole’s Life Cycle
Frogs like to eat different things at different stages of their life-cycle. This is due to them under going metamorphosis, but also because they change from living in only water as a tadpole into living in both water and on land as a frog. You can read more about the life cycle of a frog or metamorphosis.
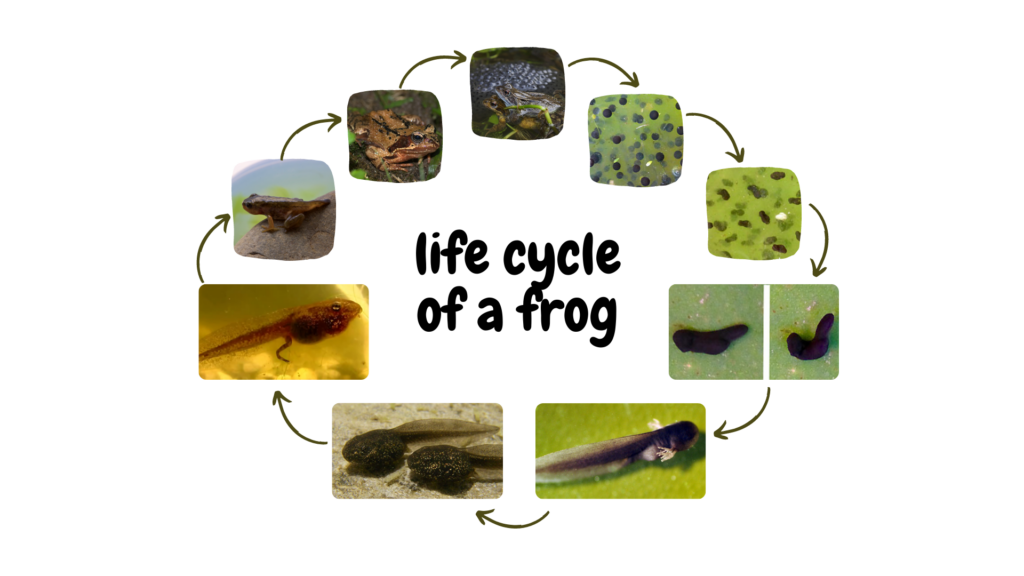
Let’s explore the eating habits of tadpoles at different stages in their life.
Small Tadpoles
Once frog spawn have developed and hatched into small tadpoles, they make their way out of the jelly layer of the egg. New hatchlings can look like this:

Hatchlings eat algae by scraping it off the surface of water plants and rocks. At this stage in their life cycle they are mainly herbivorous.
If you ever want to simulate being a young tadpole in the wild, you can play TaddyPole, where you play as a young tadpole who munches your way through a pond and avoid being eaten by predators!
Bigger Tadpoles
Once tadpoles grow bigger and begin to develop their legs, they became carnivorous and feed on small water animals.
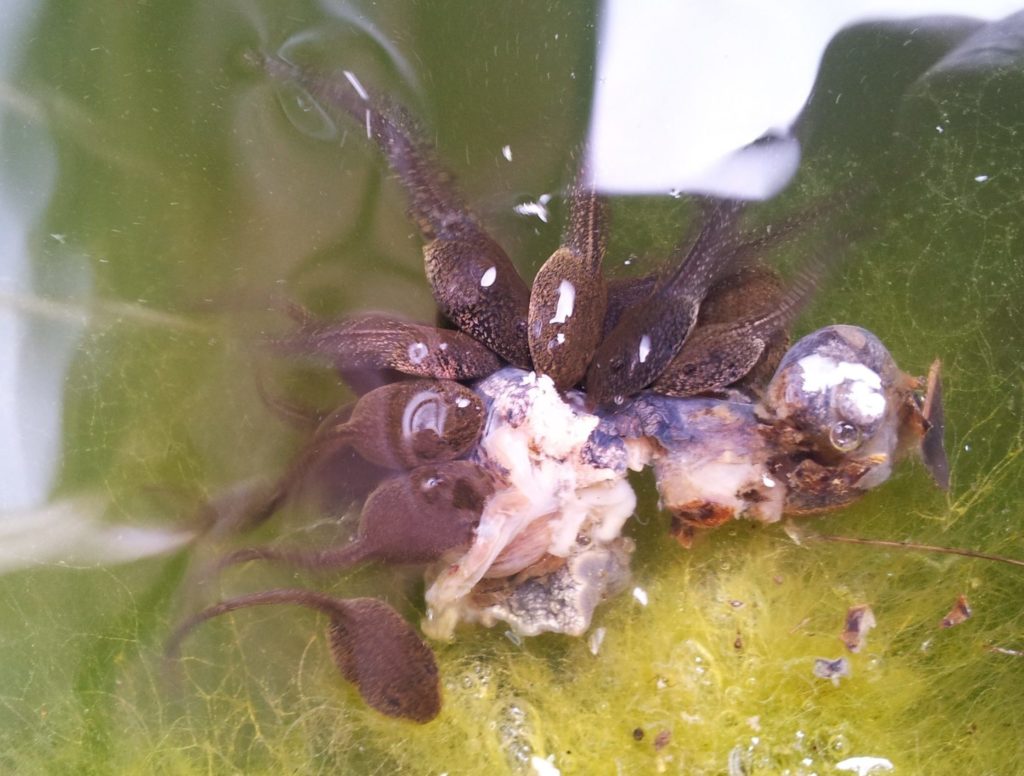
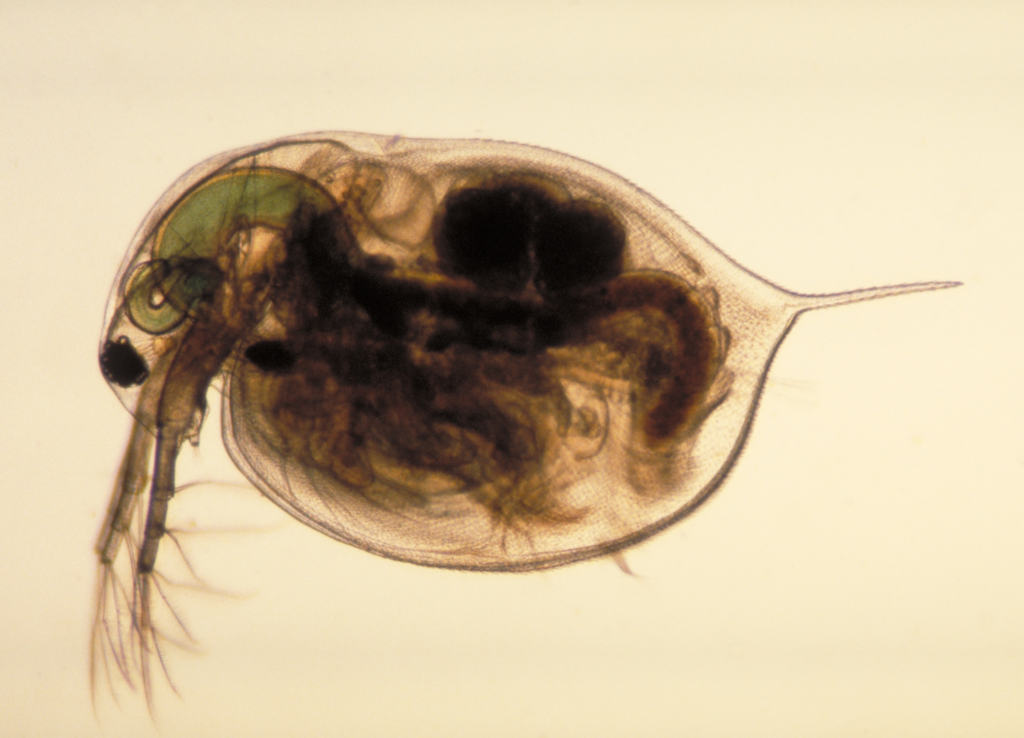

They will also eat each other if there is not enough food around! This is something to be careful of when taking care of your own tadpoles, so click here to read more about how to feed tadpoles properly when taking care of them as pets.
Froglets and Adult Frogs
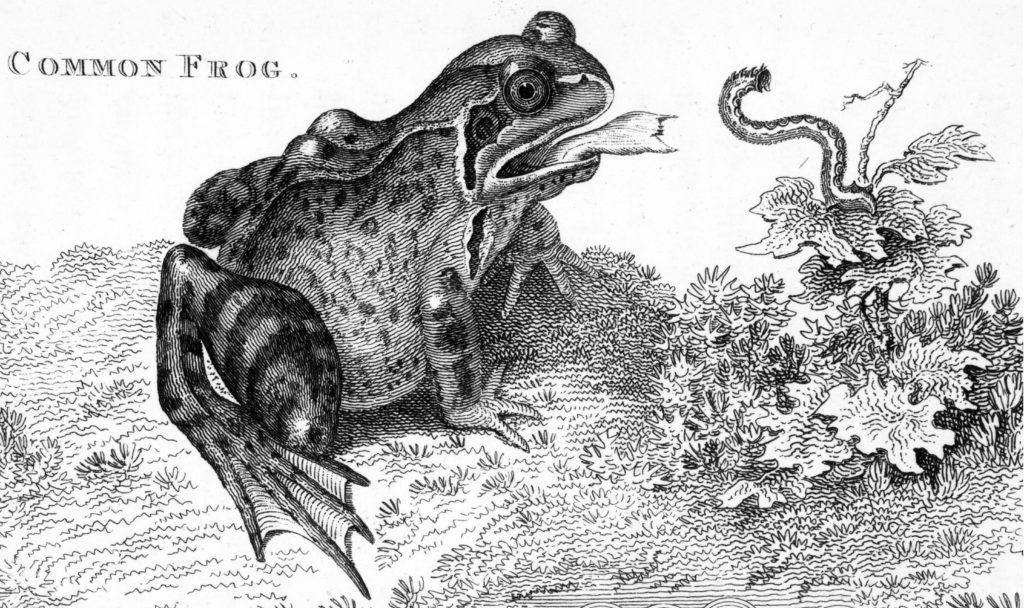
Froglets will eat small insects once they have left the pond. Adult frogs are mainly carnivorous and will also eat insects as well as slugs, snails and worms. Below is an old drawing of a frog about to catch a caterpillar with its tongue.

Quiz Time!
Results
We hope you now know more about what tadpoles like to eat! Click here to explore more topics.
#1. What do you call animals that eat both meat and plants?
#2. At what stage do tadpoles begin to eat meat?
#3. Fill in the blank: "Tadpoles eat ________ at different stages in their life cycle".
#4. Which is not an example of something that an adult frog would eat.
Remember to attribute photographs, videos or work where appropriate! This is not needed unless used online, but if you’re unsure please refer to the creative commons licence rules. For media credits for the images above, please refer to the next page.




